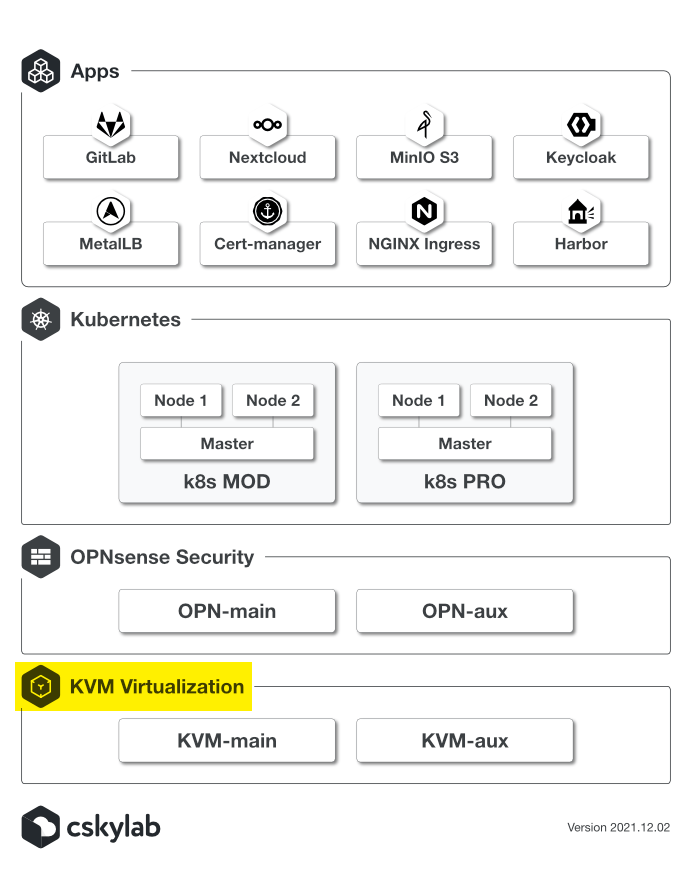
1 - KVM Virtualization
Building kvm-main & kvm-aux
This procedure explains how to build cSkyLab KVM layer infrastructure
Prerequisites
Hardware requirements
| Configuration | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 2 core cpu | 4+ core cpu |
| Memory | 16 GB | 128+ GB |
| Network | 4x1Gb | 4x10Gb+ 4x1Gb |
| Disk 1 (System) | 80 GB | 80-120 GB |
| Disk 2 (LVM) | 250 GB | 1+ TB |
Note: Additional disks can be added and managed by LVM.
Network assignements
cSkyLab virtual networking model is defined in 01-netcfg.yaml NetPlan configuration file in kvm machines. It includes the following networks:
| Network | VLAN Id | Purpose | External NIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| WAN | 909 | OPNsense WAN Uplink | yes |
| sys | 910 | System services | yes |
| sys_pfsync | 911 | OPNsense HA cluster | |
| mod_srv | 912 | Model services | |
| pro_srv | 913 | Production services | |
| usr | 914 | Users local access | optional |
| SETUP | 915 | OPNsense & KVM hosts setup access | yes |
All VLAN's are defined inside a unique uplink bond:
| Bond | VLAN Id | Purpose | External NIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| bond_csky | All (Trunk mode) | Uplink | yes |
If external managed switches are used, it is recommended to bond 2 or 4 NIC's for the uplink, as defined in NetPlan configuration file 01-netcfg.yaml.
If only two physical machines are used (kvm-main and kvm-aux), there is no need to deploy the networking model to external switches. You must then connect the bond between both machines in order to get the networking model up and running.
The physical machine hosting kvm services must have at least 4 NIC's (5 if users local access is needed) in order to provide external connections to the following networks:
- NIC 1: WAN
- NIC 2: sys
- NIC 3: SETUP
- NIC 4: bond_csky
- Optional NIC 5: usr
The recommended configuration is 4 10Gb NIC + 4 1Gb NIC connected as in the SuperMicro example provided.
Note: Before deploying kvm, you should perform in your machine a basic installation of Ubuntu 24.04 server and get the interfaces names with
networkctl status --all. Plan and modify your NetPlan configuration file01-netcfg.yamlaccording to your interfaces names.
How-to build kvm-main & kvm-aux
Setup OS from bare metal (SuperMicro example)
These procedures are examples made for SuperMicro IPMI & BIOS setup. With other hardware, you should apply analog procedures according to the software provided by your manufacturer.
NOTE: Connect only IPMI network port. To perform IPMI & Bios configuration connect only to IPMI service until OS installation is made to the physical machine.
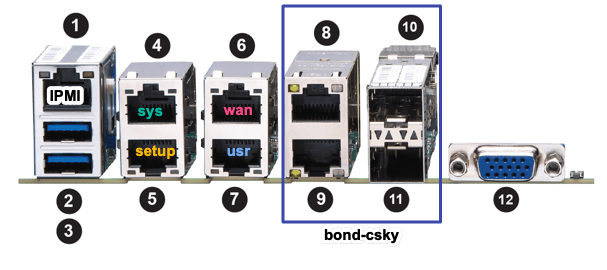
Supermicro network ports assignment:
| Port | Type | Network | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IPMI | ||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | 1Gb | sys | eno2 |
| 5 | 1Gb | setup | eno1 |
| 6 | 1Gb | wan | eno4 |
| 7 | 1Gb | usr | eno3 |
| 8 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno6 |
| 9 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno5 |
| 10 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno8 |
| 11 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno7 |
| 12 | |||
IPMI Initial settings
- Login
- Connect the IPMI port to your LAN. Take note of the IP address by your DHCP service.
- Using Firefox browser navigate to "https://IPMI_IP_address". Accept the warning messages about self-signed certificate.
- Login with
ADMINuser and the unique password supplied in "PWD" label in the sticker located at the bottom of your machine. For more information about Supermicro IPMI see:
- Set hostname
- In Configuration -> Network configure the following settings:
- Hostname:
ipmi-kvm-mainoripmi-kvm-aux - Introduce a fixed IP Address (optional).
Save
- Hostname:
- In Configuration -> Network configure the following settings:
Bios configuration
- Login to IPMI
- Start a remote console: In Remote Control -> iKVM/HTML5 start a remote console
- Open virtual keyboard: If necessary, open a virtual keyboard pressing the button down left
- Start the machine: Execute Power Control -> Set Power On to start the machine
- Enter in BIOS Setup: Press
<del>to run Setup when prompted.
- Load Optimized Defaults: Execute Save & Exit -> Restore Optimized Defaults and confirm selection.
- Set sSATA Configuration: Execute Advanced -> PCH sSATA Configuration -> sSATA Device Type -> Solid State Drive for detected SATA drives.
- Finish setup and restart the machine:
- Execute Save & Exit -> Save as User Defaults and confirm selection.
- Execute Save & Exit -> Save Changes and Reset and confirm selection.
Ubuntu 24.04 clean installation
NOTE: Connect IPMI & SETUP network ports. To perform OS installation you must connect both network ports.
Supermicro network ports assignment:
| Port | Type | Network | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IPMI | ||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | 1Gb | sys | eno2 |
| 5 | 1Gb | SETUP | eno1 |
| 6 | 1Gb | wan | eno4 |
| 7 | 1Gb | usr | eno3 |
| 8 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno6 |
| 9 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno5 |
| 10 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno8 |
| 11 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno7 |
| 12 | |||
Note: In some machine models and BIOS versions it may be required to unplug all additional disks, except system disk(s), until first OS installation is completed.
Prepare Ubuntu Server Setup USB flash disk
- Download Ubuntu Server iso file from https://ubuntu.com/download/server using
Manual server installation - Generate usb boot disk from iso file (Use balenaEtcher software in MacOS)
- Download Ubuntu Server iso file from https://ubuntu.com/download/server using
Plug USB flash disk with .iso installation into the machine
Login to IPMI
Start a remote console: In Remote Control -> iKVM/HTML5 start a remote console
Open virtual keyboard: If necessary, open a virtual keyboard pressing the button down left
Start the machine: Execute Power Control -> Set Power On to start the machine
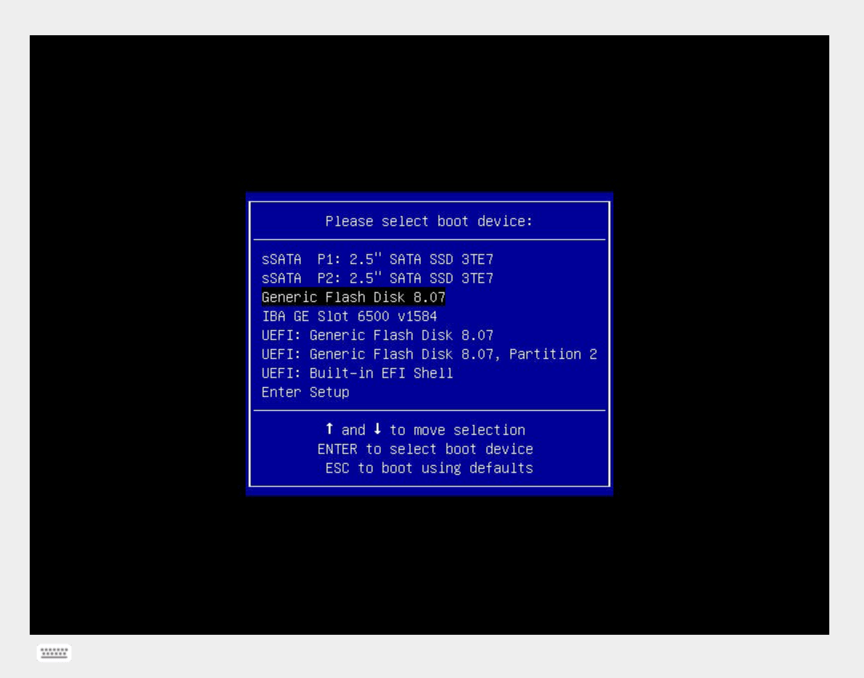
Enter in Boot Menu: Press
<F11>to invoke Boot Menu when promptedSelect Flash disk boot device and boot the machine
Follow the procedure in Utilites section Ubuntu 24.04 server setup to perform a clean installation of Ubuntu server 24.04.
Install kvm hosts
- Clone your cSkyLab installation repository in your local machine if you haven't done it before.
- Open terminal window in
kvm-mainorkvm-auxfolder, depending on what machine you're configuring. - Connect only the following NIC's
- IPMI
- SETUP
NOTE: Connect IPMI & SETUP network ports. To perform kvm initial configuration you must connect only these network ports.
Supermicro network ports assignment:
| Port | Type | Network | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IPMI | ||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | 1Gb | sys | eno2 |
| 5 | 1Gb | SETUP | eno1 |
| 6 | 1Gb | wan | eno4 |
| 7 | 1Gb | usr | eno3 |
| 8 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno6 |
| 9 | 10Gb | bond_csky | eno5 |
| 10 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno8 |
| 11 | 10Gb SPF | bond_csky | eno7 |
| 12 | |||
- Boot the machine
- Get the IP Address assigned by your DHCP (You can get it by connecting to machine console through IPMI, or looking at your DHCP server leases).
NOTE: kvm machines must be accessed by IP address when connecting from setup network. You must use always the option
-r IPaddressin csinject.sh configuration scripts.
Inject SSH keys and sudoers file
- Inject SSH keys and sudoers files by executing:
# Run csinject.sh in [ssh-sudoers] execution mode./csinject.sh -k -r IPaddress
This step injects ssh key and sudoers file into the machine.
If ssh key has not been injected before, you must provide the password for username {{ .machine.localadminusername }}@{{ .machine.hostname }} twice:
- First one to install ssh key (ssh-copy-id).
- Second one to deploy the sudoers file.
Install packages, updates and perform configuration tasks
This step performs:
- Package installation
- Updates
- Configuration files deployment
- Configuration tasks
It is required to run at least once in order to complete proper configuration. Automatic reboot is performed when finished.
To perform installation, execute from your machine repository directory:
# Run csinject.sh to inject & deploy configuration in [install] deploy mode./csinject.sh -qdm install -r IPaddress
Inject kvm hosts ssh keys into each other
From every kvm host, inject ssh keys to allow scp operations:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPaddress# From kvm-main & kvm-auxsudo ssh-copy-id kos@IPaddress
Configure storage & data protection
Create volgroup
To create Volgroup to support LVM data services, execute inside the host the following command:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPAddress# Create volgroup and thin LVM in Data Disk (/dev/sdb)sudo cs-volgroup.sh -m create -qd "/dev/sdb" -v "vgdata"
Create LVM data services
Four thin LVM data services are created with the following purposes:
| Data Service | Purpose |
|---|---|
/srv/setup | Cloud images, .iso files and other setup resources exported from kvm-main to kvm-aux |
/srv/vm-main | Resources of mirrored virtual machines, running on kvm-main and exported to kvm-aux (if present) |
/srv/vm-aux | Resources of mirrored virtual machines, running on kvm-aux (if present) and exported to kvm-main |
/srv/vmachines | Local virtual machine resources not exported |
NOTE: Resources of mirrored virtual machines will be regulary copied to its mirror host, accordingly to the schedule programmed on
cs-cron-scripts.
To create the corresponding LVM data services, execute inside the host the following commands:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPAddress# Create data servicessudo cs-lvmserv.sh -m create -qd "/srv/setup" \&& sudo cs-lvmserv.sh -m create -qd "/srv/vm-aux" \&& sudo cs-lvmserv.sh -m create -qd "/srv/vm-main" \&& sudo cs-lvmserv.sh -m create -qd "/srv/vmachines"
Download cloud-init img files
Before creating virtual machines it is required to have Ubuntu 24.04 server & OPNsense cloud-init image files in setup directories of both kvm-main and kvm-aux servers.
Note: Cloud-init image files are provided for Ubuntu server. You can generate your own cloud image file for OPNSense following the procedure "Create cloud image from .iso file" provided in
opn-main&opn-auxmachines documentation. An OPNSense cloud image file from cSkyLab is also provided in this procedure to accelerate virtual machine deployment.
To download cloud-init files use the following procedure in each server:
- Connect to kvm server:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPAddress- Execute this command inside each kvm host:# Download cloud-init imagesecho && echo "******** SOE - START of execution ********" && echo \&& cd "/srv/setup" \&& curl --remote-name https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/jammy/current/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img \&& export MC_HOST_minio="https://cloud-init_ro:vDpw3F33Kj9Pthr650rob1Y8svBTCra6@minio-promise.csky.cloud" \&& mc cp -r minio/cloud-init/opn-tpl-sysdisk.qcow2 ./ \&& echo && echo "******** EOE - END of execution ********" && echo
Backup & data protection
Pre-configured cron jobs for rsync and restic backups are available in files tpl-kvm-main-cs-cron_scripts and tpl-kvm-aux-cs-cron_scripts. You can review and modify time schedules as needed.
When kvm-main & kvm-aux machines are present, rsync cronjobs are used to achieve service HA for machines running in mirrored pools in the following way:
| Running mode | Data service | Defined in | Replicated to |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal mode: [kvm-main + kvm-aux] | |||
/srv/vm-main | kvm-main | kvm-aux | |
/srv/vm-aux | kvm-aux | kvm-main | |
| [kvm-main standalone] | |||
/srv/vm-main | kvm-main | kvm-aux (when present) | |
/srv/vm-aux | kvm-main | kvm-aux (when present) | |
| [kvm-aux standalone] | |||
/srv/vm-main | kvm-aux | kvm-main (when present) | |
/srv/vm-aux | kvm-aux | kvm-main (when present) |
To activate backup & data protection:
- In
kvm-mainconfiguration repository directory (cs-sys/kvm-main) rename filetpl-kvm-main-cs-cron_scriptstocs-cron_scripts - In
kvm-auxconfiguration repository directory (cs-sys/kvm-aux) rename filetpl-kvm-aux-cs-cron_scriptstocs-cron_scripts - Inject & deploy configuration to both machines executing:
# Inject & deploy configuration files./csinject.sh -qd -r IPAddress
Network configuration
- Review NetPlan configuration file
01-netcfg.yaml.
This step deploys cSkyLab virtual network configuration. Cloud-init configuration will be disabled from the next start.
Reboot is automatically performed when finished.
- Execute machine network configuration by running:
# Run csinject.sh to inject & deploy configuration in [net-config] deploy mode./csinject.sh -qdm net-config -r IPaddress
After network configuration, the default gateway will be statically assigned to sys internal network. To keep contact with the kvm machine, you must be connected to the same SETUP network without any router in the middle.
- To get the IP Address assigned by your DHCP, check leases in your router or connect to console through IPMI and execute
networkctl status --all. The new address insetupnetwork will be assigned to interfacebr_setup.
NOTE: If you loose network connection to your kvm machine, your must login via console and use the previous NetPlan yaml configuration file in directory
/etc/netplan.
Configure bridges and storage pools
Create virtual bridges
Review file brvlan_list.txt with virtual bridges list and inject configuration into the machine:
br_wanbr_sysbr_sys_pfsyncbr_mod_srvbr_pro_srvbr_usrbr_setup
# Inject and deploy machine configuration files./csinject.sh -qd -r IPaddress
Connect inside the machine:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPaddressTo **create** virtual briges, execute inside the machine the following command:# Apply virtual bridges:sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -m set-bridges
Create virtual storage pools
Review file dirpool_list.txt with virtual storage pools and inject configuration into the machine:
setupvm-mainvm-auxvmachines
# Inject and deploy machine configuration files./csinject.sh -qd -r IPaddress
Connect inside the machine:
# Connect to the machine./csconnect.sh -r IPaddressTo **create** virtual storage pools, execute inside the host the following command:# Apply storage pools:sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -m set-stpools
Create virtual machines
cSkyLab virtual machines are distributed and pre-configured in the following way:
kvm-main:
| Virtual Machine | Data service | Replicated to | Default CPU | Default RAM | Default Data Disk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| opn-main | /srv/vm-main | kvm-aux | 2 | 4096 | |
| k8s-mod-master | /srv/vm-main | kvm-aux | 2 | 4096 | |
| k8s-mod-n1 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-mod-n3 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-pro-master | /srv/vm-main | kvm-aux | 2 | 4096 | |
| k8s-pro-n1 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-pro-n3 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB |
kvm-aux:
| Virtual Machine | Data service | Replicated to | Default CPU | Default RAM | Default Data Disk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| opn-aux | /srv/vm-aux | kvm-main | 2 | 4096 | |
| mcc | /srv/vm-aux | kvm-main | 2 | 2048 | |
| k8s-mod-n2 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-mod-n4 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-pro-n2 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB | |
| k8s-pro-n4 | /srv/vmachines | 4 | 32768 | 256 GB |
To create virtual machines inside kvm-main & kvm-aux use the following procedure.
Check virtual machines defaults (Optional)
Each virtual machine has its own configuration directory files in both kvm-main & kvm-hosts.
You can change CPU RAM & Data Disks default configurations if needed by editing cloud-virt-install.sh files.
Example: If you want to adjust configuration for virtual machine k8s-mod-n1:
- Edit configuration file
cs-sys/kvm-main/k8s-mod-n1/cloud-virt-install.sh:
# ...# ...# ...virt-install --name "${vmachine_name}" \--virt-type kvm --memory 32768 --vcpus 4 \--boot hd,cdrom,menu=on --autostart \--disk path="${vmachines_path}/${vmachine_name}-setup.iso",device=cdrom \--disk path="${vmachines_path}/${vmachine_name}-sysdisk.qcow2",device=disk \--disk path="${vmachines_path}/${vmachine_name}-datadisk.qcow2",device=disk,size=256 \--os-variant ubuntu24.04 \--network network=br_mod_srv \--console pty,target_type=serial \--noautoconsole
- You can change values for:
- --memory 32768 (RAM)
- --vcpus 4 (CPU's)
- size=256 (Data Disk)
Create virtual machines in kvm-main
Execute this command from inside kvm-main to create virtual machines:
# Create kvm-main virtual machinesecho && echo "******** SOE - START of execution ********" && echo \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n opn-main -i /srv/setup/opn-tpl-sysdisk.qcow2 -s NONE -p /srv/vm-main \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-mod-master -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vm-main \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-mod-n1 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-mod-n3 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-pro-master -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vm-main \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-pro-n1 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-pro-n3 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& echo && echo "******** EOE - END of execution ********" && echo
Note: Before continuing, look in your DHCP leases in your router and take note of the IPAddress assigned to OPNsense. This is the machine to be configured as
opn-mainin OPNsense cluster.
- Connect via browser to
opn-mainwith the IPAddress assigned and login with:- Username: root
- Password: NoFear21
- Go to System -> Configuration -> Backups
- Click
Choose file& select filecs-sys/opn-cluster/config-opn-main.genesis-xxxxx.xmlto restoreopn-mainconfiguration from XML file. - Click
Restore configurationto restore configuration from XML file.
Execute this command from inside kvm-aux to create virtual machines:
# Create kvm-aux virtual machinesecho && echo "******** SOE - START of execution ********" && echo \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n opn-aux -i /srv/setup/opn-tpl-sysdisk.qcow2 -s NONE -p /srv/vm-aux \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n mcc -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vm-aux \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-mod-n2 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-mod-n4 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-pro-n2 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& sudo cs-kvmserv.sh -qm vm-create -n k8s-pro-n4 -i /srv/setup/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img -s 80G -p /srv/vmachines \&& echo && echo "******** EOE - END of execution ********" && echo
Note: Before continuing, look in your DHCP leases in your router and take note of the IPAddress assigned to OPNsense. This is the machine to be configured as
opn-auxin OPNsense cluster.
- Connect via browser to
opn-auxwith the IPAddress assigned and login with:- Username: root
- Password: NoFear21
- Go to System -> Configuration -> Backups
- Click
Choose file& select filecs-sys/opn-cluster/config-opn-aux.genesis-xxxxx.xmlto restoreopn-auxconfiguration from XML file. - Click
Restore configurationto restore configuration from XML file.
License
Copyright © 2023 cSkyLab.com ™
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.